Tsavo highway (location): Difference between revisions
From Halopedia, the Halo wiki
Halopediaman (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
(Initiating site-wide removal of levelname template. Feel free to do the same.) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Ratings}} | {{Ratings}} | ||
{{References}} | {{References}} | ||
<center>''"Tsavo Highway" redirects here. For the campaign level, see [[Tsavo Highway ( | <center>''"Tsavo Highway" redirects here. For the campaign level, see [[Tsavo Highway (level)]].''</center> | ||
[[File:Highway_2.jpg|250px|thumb|The Tsavo Highway, damaged during the [[Battle of Earth]].]] | [[File:Highway_2.jpg|250px|thumb|The Tsavo Highway, damaged during the [[Battle of Earth]].]] | ||
'''Tsavo Highway'''<ref name="level">'''[[Halo 3]]''', level '' | '''Tsavo Highway'''<ref name="level">'''[[Halo 3]]''', level ''[[Tsavo Highway (level)|Tsavo Highway]]</ref> is a highway that replaced the old [[Republic of Kenya|Kenyan]] international trunk road [[Wikipedia:A23 road (Kenya)|A23]]. This highway bears the name "[[Tsavo]]" because it bisects the southern part of the [[Wikipedia:Tsavo West National Park|Tsavo West national park]], it doesn't actually pass through the town of [[Wikipedia:Tsavo|Tsavo]] as is commonly mistaken. <ref>'''[[Halo 3]]''', level ''[[The Storm]]</ref> | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
Roads are the primary communication links to all sectors of the economy and the population. It is widely recognized that an efficient road infrastructure is a prerequisite for economic and social development. In the twenty-first century, roads are referred to by a wide range of names and descriptions - National, Main, Trunk, District, City, Rural, Local, Access etc. However, roads can be broadly categorized according to the Authority primarily responsible for their management as national, district, urban and special purpose roads. National Roads are the main highways of the classified road network comprising Class A, B, C roads and are managed by the Roads Department of the Ministry of Roads and Public Works. These roads provide mobility in a national context and the traffic on these roads is usually associated with longer travel distances. Hence design provisions for these roads allow for relatively higher speeds and minimal interference with through traffic i.e. restricted access. Class A are international trunk roads linking international boundaries or terminating at international ports e.g. Malaba-Nairobi-Mombasa Road.{{citation needed}} | Roads are the primary communication links to all sectors of the economy and the population. It is widely recognized that an efficient road infrastructure is a prerequisite for economic and social development. In the twenty-first century, roads are referred to by a wide range of names and descriptions - National, Main, Trunk, District, City, Rural, Local, Access etc. However, roads can be broadly categorized according to the Authority primarily responsible for their management as national, district, urban and special purpose roads. National Roads are the main highways of the classified road network comprising Class A, B, C roads and are managed by the Roads Department of the Ministry of Roads and Public Works. These roads provide mobility in a national context and the traffic on these roads is usually associated with longer travel distances. Hence design provisions for these roads allow for relatively higher speeds and minimal interference with through traffic i.e. restricted access. Class A are international trunk roads linking international boundaries or terminating at international ports e.g. Malaba-Nairobi-Mombasa Road. {{citation needed}} | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
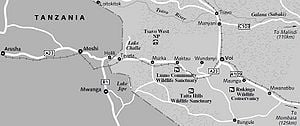
[[File:Map.JPG|300px|thumb|21<sup>st</sup> century map showing A23 (Tsavo highway) and the locations of Arusha, Voi, Tsavo, and Mombasa]] | [[File:Map.JPG|300px|thumb|21<sup>st</sup> century map showing A23 (Tsavo highway) and the locations of Arusha, Voi, Tsavo, and Mombasa]] | ||
In 1998, Kenya and its Partner States agreed on the East African Road Network Project. The project consists of five major regional road corridors, two are briefly described | In 1998, Kenya and its Partner States agreed on the East African Road Network Project. The project consists of five major regional road corridors, two are briefly described below. The [[Mombasa]] - Malaba - Katuna corridor and its feeder links consisting of the Mombasa - Lunga Lunga - Tanga, the [[Voi]] - Mwatate - Taveta - Holili - Himo, and three other links. The Dar es Salaam - Dodoma - Isaka - Mutukula - Masaka corridor with the feeder links being the Chalinze - Segera - Himo - Moshi - [[Arusha]], the Dar es Salaam - Mtwara - Mbamba Bay and Nzega - Tabora - Mbeya, and one other link.<ref>[http://www.krb.go.ke/index.php/component/content/article/15-road-info/17-east-african-road-network '''Kenya Roads Board''' - ''THE EAST AFRICAN ROAD NETWORK'']</ref> | ||
The A23 resides in the western edge of the Coastal province of Kenya and is part of both the Mombasa - Malaba - Katuna, and the Dar as Salaam - Dodoma - Isaka - Mutukula - Masaka corridors according to modern-day geographical boundaries. In the twenty-first century, the A23 road begins at Voi and passes on to Arusha that is in Tanzania. Smaller towns lying between these population centres are, Maktau, Murka, Taveta, Holili(Tanzania) and Moshi(Tanzania) in that order. There is also a railway that runs the same route. Highway A23 joins directly onto highway A109 at Voi, and connects Nairobi and Mombasa. By the 21st century, this and all other national roads were maintained under the Roads Department of Ministry of Roads and Public Works, affiliated with the Kenya Roads Board.{{citation needed}} | The A23 resides in the western edge of the Coastal province of Kenya and is part of both the Mombasa - Malaba - Katuna, and the Dar as Salaam - Dodoma - Isaka - Mutukula - Masaka corridors according to modern-day geographical boundaries. In the twenty-first century, the A23 road begins at Voi and passes on to Arusha that is in Tanzania. Smaller towns lying between these population centres are, Maktau, Murka, Taveta, Holili(Tanzania) and Moshi(Tanzania) in that order. There is also a railway that runs the same route. Highway A23 joins directly onto highway A109 at Voi, and connects Nairobi and Mombasa. By the 21st century, this and all other national roads were maintained under the Roads Department of Ministry of Roads and Public Works, affiliated with the Kenya Roads Board.{{citation needed}} | ||
Revision as of 17:28, October 20, 2010
| This article does not have enough inline citations and/or does not adhere to the proper citation format. You can help Halopedia by adding citations. |

Tsavo Highway[1] is a highway that replaced the old Kenyan international trunk road A23. This highway bears the name "Tsavo" because it bisects the southern part of the Tsavo West national park, it doesn't actually pass through the town of Tsavo as is commonly mistaken. [2]
Background
Roads are the primary communication links to all sectors of the economy and the population. It is widely recognized that an efficient road infrastructure is a prerequisite for economic and social development. In the twenty-first century, roads are referred to by a wide range of names and descriptions - National, Main, Trunk, District, City, Rural, Local, Access etc. However, roads can be broadly categorized according to the Authority primarily responsible for their management as national, district, urban and special purpose roads. National Roads are the main highways of the classified road network comprising Class A, B, C roads and are managed by the Roads Department of the Ministry of Roads and Public Works. These roads provide mobility in a national context and the traffic on these roads is usually associated with longer travel distances. Hence design provisions for these roads allow for relatively higher speeds and minimal interference with through traffic i.e. restricted access. Class A are international trunk roads linking international boundaries or terminating at international ports e.g. Malaba-Nairobi-Mombasa Road. [citation needed]
History
In 1998, Kenya and its Partner States agreed on the East African Road Network Project. The project consists of five major regional road corridors, two are briefly described below. The Mombasa - Malaba - Katuna corridor and its feeder links consisting of the Mombasa - Lunga Lunga - Tanga, the Voi - Mwatate - Taveta - Holili - Himo, and three other links. The Dar es Salaam - Dodoma - Isaka - Mutukula - Masaka corridor with the feeder links being the Chalinze - Segera - Himo - Moshi - Arusha, the Dar es Salaam - Mtwara - Mbamba Bay and Nzega - Tabora - Mbeya, and one other link.[3]
The A23 resides in the western edge of the Coastal province of Kenya and is part of both the Mombasa - Malaba - Katuna, and the Dar as Salaam - Dodoma - Isaka - Mutukula - Masaka corridors according to modern-day geographical boundaries. In the twenty-first century, the A23 road begins at Voi and passes on to Arusha that is in Tanzania. Smaller towns lying between these population centres are, Maktau, Murka, Taveta, Holili(Tanzania) and Moshi(Tanzania) in that order. There is also a railway that runs the same route. Highway A23 joins directly onto highway A109 at Voi, and connects Nairobi and Mombasa. By the 21st century, this and all other national roads were maintained under the Roads Department of Ministry of Roads and Public Works, affiliated with the Kenya Roads Board.[citation needed]
When the industrial revolution of East Africa begun, everything that was transported to and from Mombasa had to be mediated by Voi to Nairobi and Dodoma in the Republic of Tanzania. This caused Voi to be greatly influenced by the revolution and it co-evolved industrially with Mombasa. Because of the increased heavy traffic from and to Voi, the old national A23 highway had fallen into disrepair. Under the authority of Tterrab Industries, it is decided to construct an entirely new highway, though most prefer the name Tsavo Highway rather than the four-digit code simply due to the fact that it is easier to recognize. Instead of replacing the A23, it was decided to be built parallel to it, thus allowing traffic to flow uninterrupted. The 'new' highway is an approximate 1.2 km NW parallel to the A23. In the twenty-sixth century, the old A23 was abandoned and only still used by the local farmers to avoid the heavy traffic.[citation needed]
By the 26th century, the road is managed by Tterrab Highway Administration.[1] The GWC Trans-African Pipelines travel along the length of the Tsavo Highway, carrying water from the main Global Water Campaign from their water processing plant in the Tanzanian jungles to Voi and from there across the rest of Africa.[4]
Covenant Invasion
- Main article: Battle of Voi
On October 2552, when the New Mombasa Orbital Elevator collapsed, debris including support rings and cables rained down to the highway, damaging it at multiple points. Later in the Battle of Earth, the Covenant Loyalist invaders occupied and barricaded the highway with Wraith tanks, Brute Choppers, and infantry formations, thereby denying access both to and from Voi; at least from the west. However, John-117 and the UNSC Marine Corps assaulted the highway, retaking it and reaching Voi.[1]
Trivia
- Tsavo is notable in that it was the site of the most famous instance of man eating lion attacks in the late 19th century as detailed in the book "Man-Eaters of Tsavo." More than 140 workers perished in the building of the railway. The event was made into the film The Ghost and the Darkness.
- The third campaign level of Halo 3, Tsavo Highway, is set at Tsavo Highway. The level takes place on a section of this highway between Maktau and Voi with the Crow's Nest being located in a hill near the town of Wundanyi.
Gallery
The United Nations Space Command charges the Covenant Loyalist-held Tsavo Highway.
- Tough luck skull.jpg.jpeg
The GWC pipelines along the highway.
Voi Municipal Water Pump House 03 near Voi.